Research and development
| Kyushu Electric has been engaged in R&D to address the prevention of global warming, including the development of fuel cells and batteries for electric vehicles. Each of these developments call for early realization for practical use. |
| • R&D into solid electrolyte fuel cell | |
|
This fuel cell utilizes the reaction of hydrogen against water electrolysis as its source for power generation. Advantages of the cell include high energy-efficiency, low noise levels, low vibration, and low air pollutant emissions. Kyushu Electric also conducts R&D into Solid Oxide Fuel Cells (SOFC). The operation temperature of SOFC is high (about 1,000 degrees celcius);thus, development of a large capacity SOFC/GT(gas turbine) combined cycle plant is expected to occur. |
 Solid Oxide Fuel Cell (SOFC) |
|
||
|
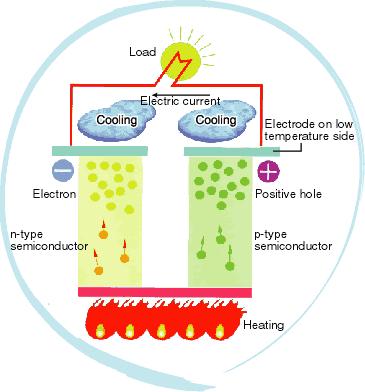
Kyushu Electric is currently researching the applicability of thermoelectric conversion elements, which convert thermal energy to electric energy, to recover thermal energy from power plant emissions, as one way to more effectively utilize unused energy. Kyushu Electric conducts comprehensive R&D ranging from the thermoelectric conversion elements to the thermoelectric energy conversion systems, including the development of new materials with better efficiency, lower costs and better environmental friendliness, as well as evaluation of heat pipe applicability as a heat recovery method. |
|
||
|
| • Development of the electric bus | |
| Kyushu Electric has strongly encouraged R&D into electric vehicles because of their environmental advantages, including low NOx and CO2 emissions and reduced noise levels. In fiscal 1999, one of Japan's largest electric buses was successfully developed, with a seating capacity of 28. The bus will be used for tours within the premises of Genkai Nuclear Power Station. |

|
|
|||
| Kyushu Electric has also worked on development of highly efficient lithium batteries for electric vehicles. In fiscal 1999, Kyushu Electric produced a prototype of 1kW-class module batteries and confirmed that these batteries have a storage capacity three times higher than existing lead batteries. The next goal in development is the packaging of module batteries, to make them commercially available within two years. |

|
||
|
||
|
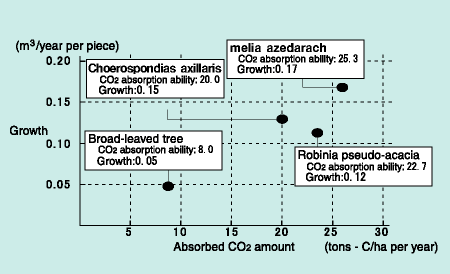
Another countermeasure for global warming is the further utilization of plants to absorb CO2. The melia azedarach tree is excellent in CO2 absorption, and grows naturally throughout Kyushu in areas below an altitude of 600m. Along with zelkova and paulownia trees, used for construction and furniture making, melia azedarach has high potential added value. Kyushu Electric has used tissue culture to mass propagate young melia azedarach trees to benefit from their high CO2 absorption ability and good quality as bulk lumber, and planted them on Kyushu Electric land. Evaluation of the trees' CO2 absorption ability is now underway, along with R&D into the establishment of afforestation technology. |
| [CO2 absorption ability of melia azedarach trees] | ||||
|
||||
|
|
|



 This mark means acrobat data.
This mark means acrobat data.